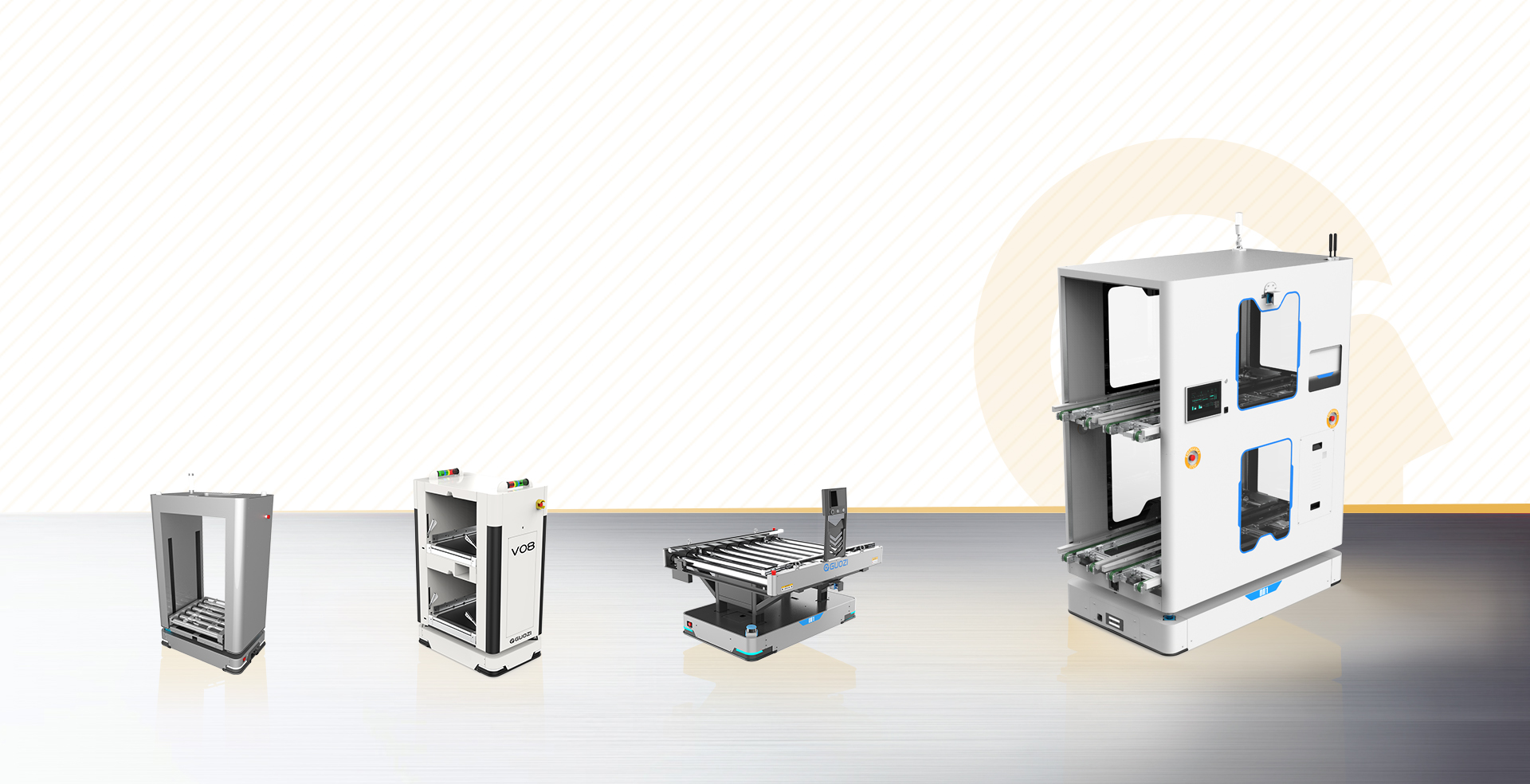
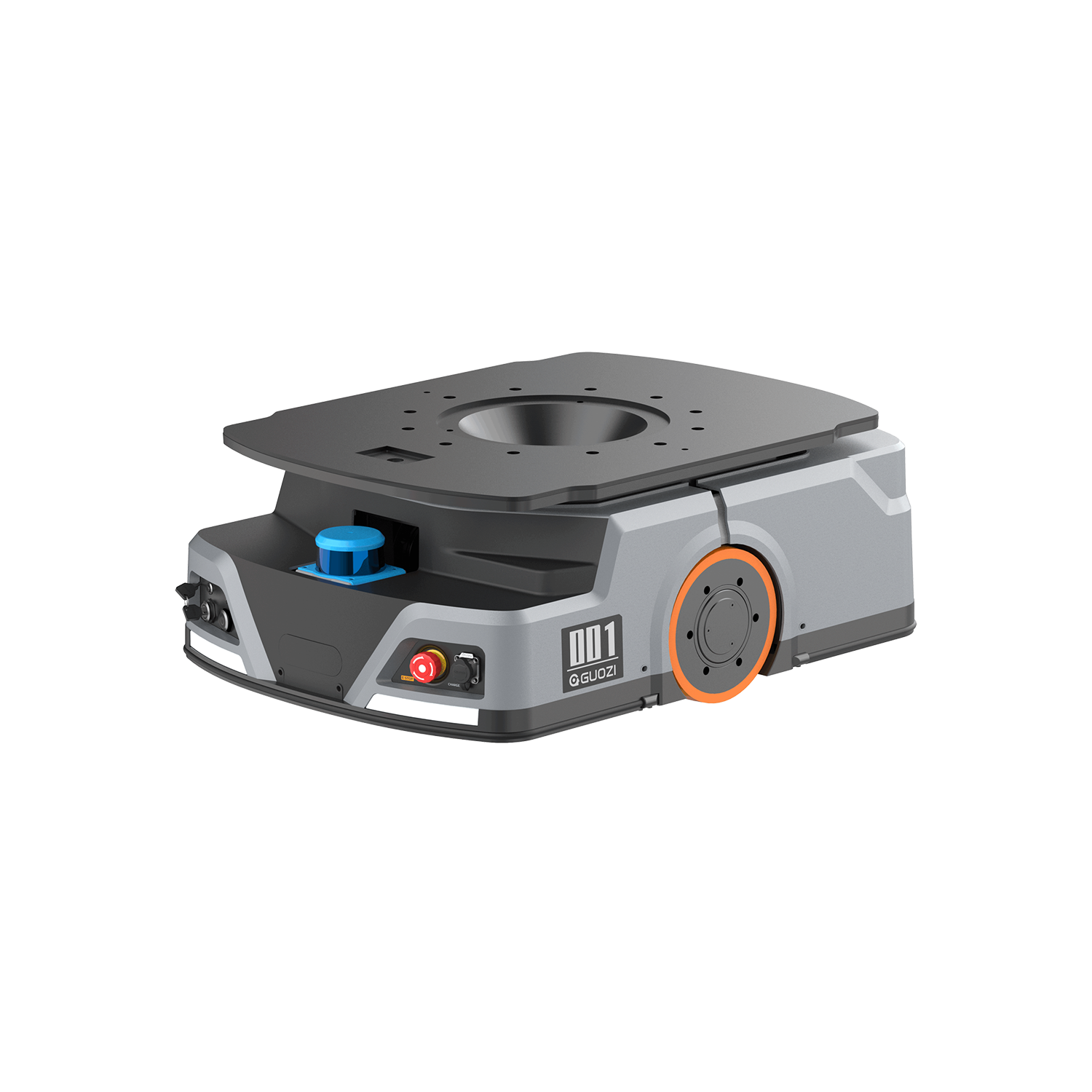
AGVs offer a number of advantages in warehousing and manufacturing.
Improve efficiency and productivity
Because AGVs can operate autonomously, they can increase efficiency and productivity, and they are predictable and reliable for repetitive tasks.AGVs eliminate unnecessary walking and the physical labor of transporting materials. They also set the pace for workers, allowing employees to focus on the task.AGVs, like collaborative mobile robots, guide employees through each task, reducing human error, which helps improve order picking accuracy and minimize lost and misplaced product. By using artificial intelligence to optimize routes and prioritize work, collaborative mobile robots can improve resource utilization.
Cost stability
AGVs are usually calculated on a per unit or lease term cost basis, and therefore have less fluctuating costs than labor, which fluctuates based on market conditions and demand.
Flexibility
Some AGVs have the flexibility to change routes with ease (whereas others require rewiring of conductors or other infrastructure to adjust the vehicle's route). Automated guided vehicles are also a scalable solution, with the ability to add additional units as needed.
Requires less space
AGVs take up less space than other automation solutions such as conveyor systems. Some AGVs are smaller than traditional warehouse equipment, such as forklifts, so they allow for floor layouts with narrower aisles and improved space utilization.
Increased safety
Finally, AGVs are a safe automation solution for warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing facilities.AGVs are equipped with sensors to avoid collisions. Advanced AGVs like AMR have intelligent routing capabilities that allow them to plan the most efficient path through a warehouse or facility, reducing aisle congestion and preventing injuries.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are uniquely designed to automate tasks that do not require human involvement. They automate long walks in warehouses, set the pace for workers, and eliminate the physical exertion of traditional manual labor.